-
Research Paper

-
A numerical study on the full-face excavation of tunnel with RCS (Rebar Coupled Shotcrete)
RCS (Rebar Coupled Shotcrete)를 적용한 터널 전단면굴착에 대한 수치해석적 연구
-
Donghyun Kim, Jinwoo Jung, Sangmin Na, Sangpil Lee
김동현, 정진우, 나상민, 이상필
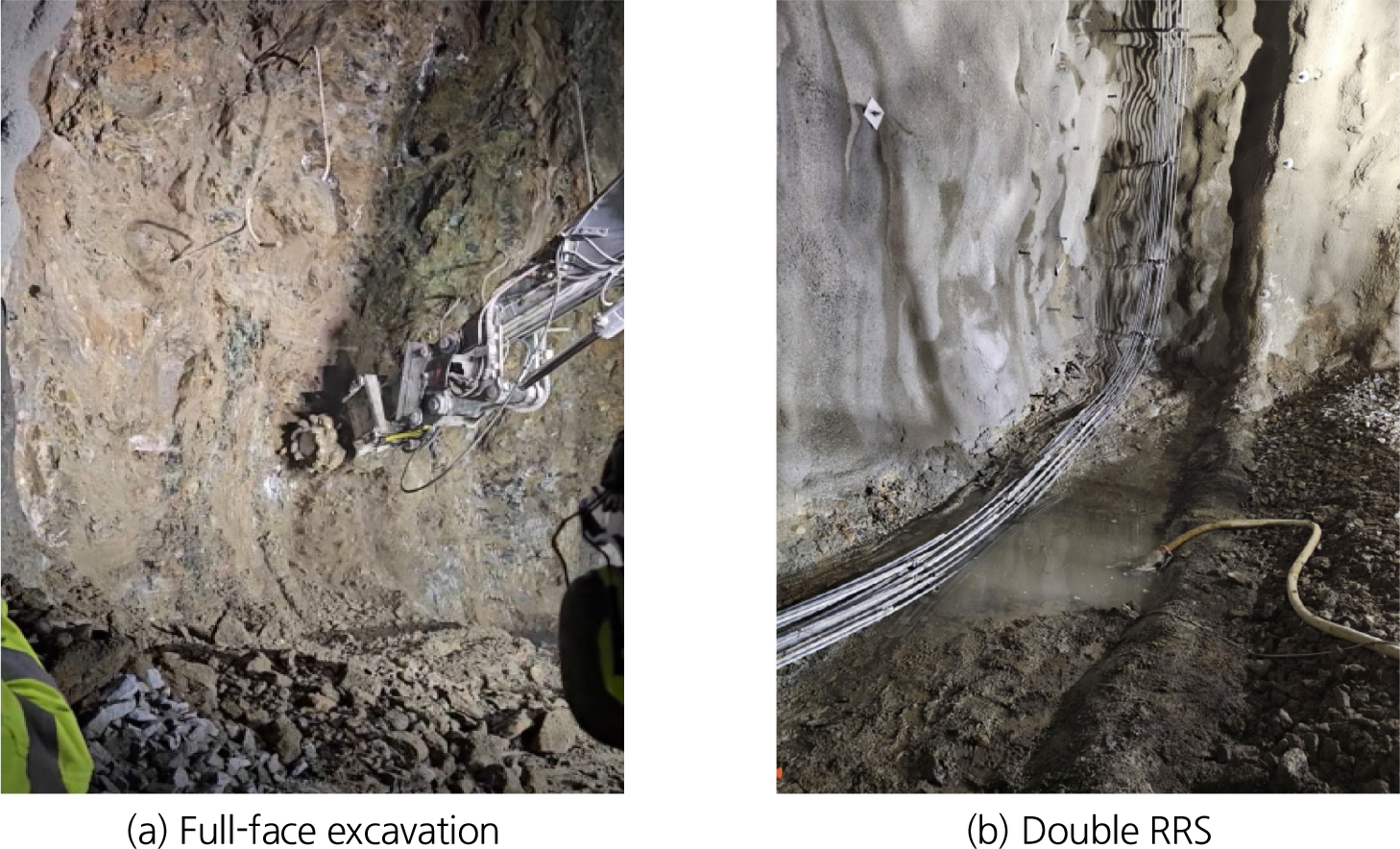
- RRS (Reinforced Ribs of Shotcrete) is a support method applied in poor rock mass conditions with a Q-value of 0.1 or less. …
RRS (Reinforced Ribs of Shotcrete)는 Q값 0.1 이하의 불량한 암반 조건에서 적용되는 터널 지보 방법이다. 1980년대 노르웨이에서 CCA (Cast Concrete Arches)를 대체하기 …
- RRS (Reinforced Ribs of Shotcrete) is a support method applied in poor rock mass conditions with a Q-value of 0.1 or less. It was introduced in Norway during the 1980s to replace CCA (Cast Concrete Arches) and was officially adopted as a substitute for CCA in the revised Q-System of 2012. In this study, we proposed the RCS (Rebar Coupled Shotcrete), an improved support method tailored to Korean tunneling conditions. RCS integrates rebars with rock bolts, embedding them within shotcrete to form a unified support system. With the increasing application of full-face excavation in poor rock mass conditions, driven by advances in tunneling equipment and support technologies, this research investigated the support performance of RCS in full-face excavation through numerical analysis. For this purpose, methods for estimating the elastic modulus of high-strength shotcrete and determining the composite strength of RCS are presented. The study compared and analyzed tunnel stability across various scenarios, considering rock mass classifications (grades 4-1 and 5-1), excavation methods (partial excavation and full-face excavation), support types (general shotcrete at 21 MPa, high-strength shotcrete at 35 MPa, and RCS), and tunnel depth. The results demonstrated that under full-face excavation conditions, the application of RCS improved tunnel stability.
- COLLAPSE
RRS (Reinforced Ribs of Shotcrete)는 Q값 0.1 이하의 불량한 암반 조건에서 적용되는 터널 지보 방법이다. 1980년대 노르웨이에서 CCA (Cast Concrete Arches)를 대체하기 위해 현장에 도입되었으며, 2012년 개정된 Q-System에서 공식적으로 CCA를 대체하였다. RRS를 국내 실정에 맞게 개선한 RCS (Rebar Coupled Shotcrete)는 철근을 록볼트와 연결하여 숏크리트 내부에 매립함으로써 일체화된 지보를 형성하여 터널의 안정성을 향상시킨다. 최근 터널 장비의 대형화와 지보기술의 발달로 불량한 암반에서도 전단면굴착 적용이 확대됨에 따라, 본 연구에서는 전단면굴착에서의 RCS 지보효과를 수치해석을 통해 검토하였다. 이를 위해 고강도 숏크리트의 탄성계수 산정과 RCS 합성강도 결정 방법을 제시하였고, 암반등급(4-1 type, 5-1 type), 굴착방법(분할굴착, 전단면굴착), 지보 종류(일반 숏크리트 21 MPa, 고강도 숏크리트 35 MPa, RCS), 터널 심도를 변수로 설정하여 각 해석 사례의 안정성을 비교·분석하였다. 해석 결과, 전단면굴착 조건에서 RCS 적용 시 터널 안정성이 향상되는 것을 확인하였다.
-
A numerical study on the full-face excavation of tunnel with RCS (Rebar Coupled Shotcrete)
-
Research Paper
-
Stability analysis of circular shaft based on inclination and discontinuity dip
수직구 경사도와 불연속면 경사에 따른 안정성 분석
-
Soojeong Kim, Hyuksang Jung, Jinsuck Kim, Jaekook Lee
김수정, 정혁상, 김진석, 이재국
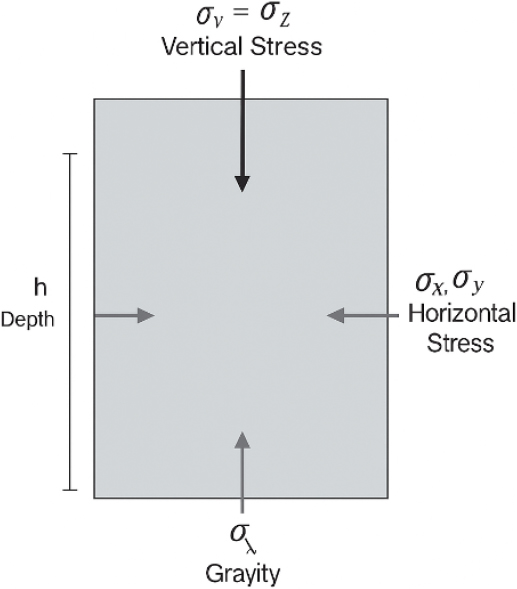
- The stability of circular vertical shafts, while benefiting from stress arching, is highly susceptible to shear-driven kinematic failure in rock masses containing …
원형 수직구는 주변 응력 아칭(Stress Arching) 효과로 구조적 안정성이 높게 평가되나, 절리 및 단층과 같은 우세 불연속면(Predominant Discontinuities)의 존재로 인해 전단 구동형 …
- The stability of circular vertical shafts, while benefiting from stress arching, is highly susceptible to shear-driven kinematic failure in rock masses containing predominant discontinuities. Conventional continuum methods, such as FEM, inherently fail to accurately predict these structurally-controlled movements due to their inability to explicitly model large-strain block interaction and separation. This study overcomes this limitation by employing the Three-Dimensional Distinct Element Method (3DEC) to quantitatively assess stability, focusing on the combined effects of shaft inclination (θs), representing construction tolerance, and discontinuity dip angle (θd), representing geological structure. A systematic parametric analysis was conducted, varying θs (0° to 15°), θd (30° to 60°), and joint shear stiffness (Ks from 0.5 to 50.0 MPa/mm). The results demonstrated that the maximum horizontal displacement in the discontinuous model was approximately 44% higher than in the intact rock model, providing clear quantitative evidence that stability is governed predominantly by the structural properties of the joints rather than the rock matrix strength. Critically, the peak displacement (1.50 mm) was identified not at the maximum analyzed tolerance, but at a minor shaft inclination of θs = 5° (θd = 60° for Against Dip), establishing the novel finding of a Critical Geometric Misalignment Condition within standard construction limits. Displacement sensitivity reached its peak when the angular difference between the shaft axis and the discontinuity plane approached 45°, which is attributed to the geometric characteristics of stress redistribution and the reduction of the arching effect in circular openings. Furthermore, the Ks analysis confirmed a Stiffness Saturation phenomenon, indicating that stability control shifts from elastic stiffness to the joint’s residual shear strength above a certain threshold. Rock bolt analysis verified an asymmetric increase in axial forces under misalignment. These findings strongly suggest that Differential Support Systems (e.g., increased rockbolt length to 6.0 m and 20% increase in shotcrete thickness) must be deployed in kinematically vulnerable shaft sections identified by the established 5° misalignment criterion.
- COLLAPSE
원형 수직구는 주변 응력 아칭(Stress Arching) 효과로 구조적 안정성이 높게 평가되나, 절리 및 단층과 같은 우세 불연속면(Predominant Discontinuities)의 존재로 인해 전단 구동형 운동학적 파괴(Kinematic Failure)에 근본적으로 취약하다는 문제점이 있다. 기존의 유한요소법(FEM) 등의 연속체 해석 기법은 암반 블록 간의 명시적인 상호작용 및 대변위를 모사할 수 없어 이러한 구조적 불안정성을 정확히 예측하는 데 그 한계가 명확하므로 본 연구에서는 이러한 방법론적 한계를 극복하고자 3차원 개별요소법(Three-Dimensional Distinct Element Method, 3DEC)을 적용하여, 시공 오차를 대변하는 수직구 경사도(θs)와 지질 구조를 대변하는 불연속면 경사각(θd)의 복합적 영향을 정량적으로 평가했으며, 체계적인 매개변수 분석은 θs (0–15°), θd (30–60°), 절리면 전단 강성(Ks: 0.5부터 50.0 MPa/mm까지)을 포함하여 시행하였다. 해석 결과, 불연속성 모델의 최대 수평 변위는 무결암 모델 대비 약 44% 증가율을 기록하였으며, 이는 수직구 안정성이 암반 매질 강도보다는 불연속면의 구조적 활동성에 의해 지배됨을 명확히 입증한 것이다. 특히, 최대 변위(1.50 mm)는 극한 오차 조건(15°)이 아닌, 일반 시공 허용 오차 내인 θs = 5° 조건(θd = 60°, Against Dip)에서 관찰되어, 임계 기하학적 부정합 조건이 미세한 경사 불량에서도 형성될 수 있다는 것을 규명하였다. 변위 민감도는 수직구축과 불연속면 간의 각도 차이가 약 45°에 근접할 때 최대치를 기록하며, 이는 원형 단면의 응력 재분배 특성에 기인한 기하학적 취약성을 의미한다. Ks 분석에서는 강성이 일정 수준 이상에서 변위가 포화되는 강성 포화(Stiffness Saturation) 현상이 확인되었으며, 이는 지반 거동이 탄성 강성보다 절리면의 잔류 전단 강도에 의해 주로 제어됨을 시사한다. 록볼트 축력은 기하학적 부정합 조건에서 비대칭적으로 증가했으며, 이 5° 경사 기준을 활용하여 운동학적으로 취약한 구간에 대한 정교한 리스크 맵핑과 구체화된 차등 지보 시스템(Differential Support System) 적용의 필요성을 제안하고자 한다.
-
Stability analysis of circular shaft based on inclination and discontinuity dip
-
Research Paper
-
A study on institutional improvements for optimal shield TBM selection and its application to power cable tunnels
최적 쉴드TBM 장비선정을 위한 제도개선 및 전력구 터널 적용 연구
-
Jung Joo Kim, Hee Hwan Ryu, Dong Joon Youn, Won Gyu Hwang, Kyung Jin Kim, Suk Jae Lee
김정주, 류희환, 윤동준, 황원규, 김경진, 이석재
- With the increasing national electricity demand and the implementation of the energy highway policy, the construction of power cable tunnels is expanding, …
국가 전력수요 증가와 에너지 고속도로 정책 추진에 따라 전력구 터널 건설이 확대되고 있으며, 쉴드TBM은 대도시 밀집지역과 지상 이용 제약이 큰 구간에서 핵심 …
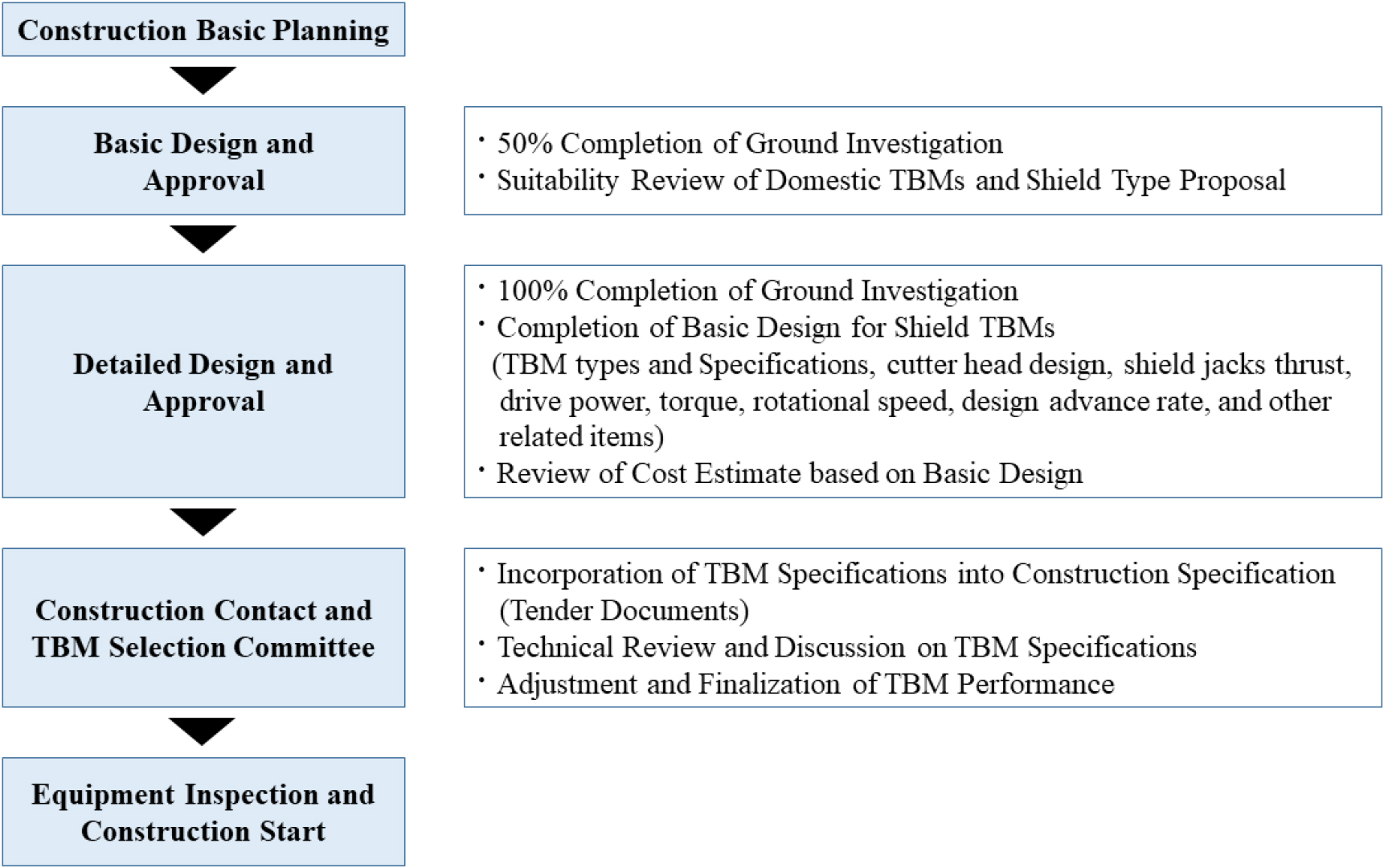
- With the increasing national electricity demand and the implementation of the energy highway policy, the construction of power cable tunnels is expanding, and shield tunnel boring machines (TBMs) are being widely adopted as a core construction method in densely populated urban areas and sections with significant surface-use constraints. This study aims to enhance the selection process of shield TBMs applied to power cable tunnels by strengthening the design procedures at the basic and detailed design stages and clearly reflecting the derived basic design specifications in the project specifications (bidding documents). In addition, a TBM selection committee was established to determine optimal machine performance through the collection and coordination of opinions from various stakeholders, including the client, designers, and manufacturers. The proposed process was applied to a large-scale transmission line construction project, through which the basic design specifications for 15 shield TBMs were clearly defined in the project specifications considering site-specific ground conditions. As a result, design-stage requirements were effectively conveyed to the manufacturing stage, leading to improvements in drive unit torque, cutterhead rotation speed, and sealing performance to approximately 122–237% of the design specifications. Furthermore, through coordination from the Equipment Selection Committee, the drive unit power drive unit performance reached, an average of approximately 104% of the design specifications across all tunnel sections, demonstrating a significant contribution to meeting the target construction schedule.
- COLLAPSE
국가 전력수요 증가와 에너지 고속도로 정책 추진에 따라 전력구 터널 건설이 확대되고 있으며, 쉴드TBM은 대도시 밀집지역과 지상 이용 제약이 큰 구간에서 핵심 공법으로 활용되고 있다. 본 연구는 전력구 터널에 투입되는 쉴드TBM 장비의 선정 프로세스를 강화하기 위해 기본 및 실시설계 단계에서의 설계 프로세스를 강화하고, 도출된 기본설계 사양을 공사시방서(입찰내역서)에 명확히 반영하도록 하였다. 장비선정위원회를 운영하여 발주기관, 설계기관, 제작기관 등 다양한 관계기관의 의견을 수렴함으로써 최적의 장비 성능을 결정하도록 하였다. 이를 대규모 송전선로 건설사업에 적용한 결과, 현장 지반조건을 고려한 15개소 쉴드TBM의 기본설계 사양을 공사시방서에 구체적으로 제시할 수 있었으며, 설계단계 요구사항이 제작단계에 효과적으로 전달되어 구동부 토크, 커터헤드 회전수 및 씰 성능이 설계사양 대비 전반적으로 122–237% 수준으로 향상되었다. 또한, 장비선정위원회 내 협의를 통해 구동부 동력성능은 모든 터널구간에서 설계사양 대비 평균 104% 수준을 만족하여, 목표 공사기간 달성에 긍정적인 효과를 기대할 수 있다.
-
A study on institutional improvements for optimal shield TBM selection and its application to power cable tunnels
-
Research Paper
-
Proposal of a CO2 emission estimation equations based on the derivation of appropriate domestic emission factors and their application: Focusing on NATM tunnel LCA (A1-A5)
국내 적정 배출계수 산정과 이를 적용한 이산화탄소 배출량 산정식 제안: NATM 터널 LCA (A1-A5)를 중심으로
-
Hae-Chan Lee, Ki-Il Song, Hong-Joo Lee
이해찬, 송기일, 이홍주
- As climate change intensifies, the frequency of natural disasters is increasing and greenhouse-gas (GHG) emissions from the industrial sector are becoming a …
기후변화로 인한 자연재해가 증가하고 산업부문 온실가스 배출 문제가 심화되면서, 각국은 IPCC 보고서 등을 바탕으로 2050 탄소중립(Net-Zero)을 선언하고 인프라 부문에서도 탄소 감축 전략을 …
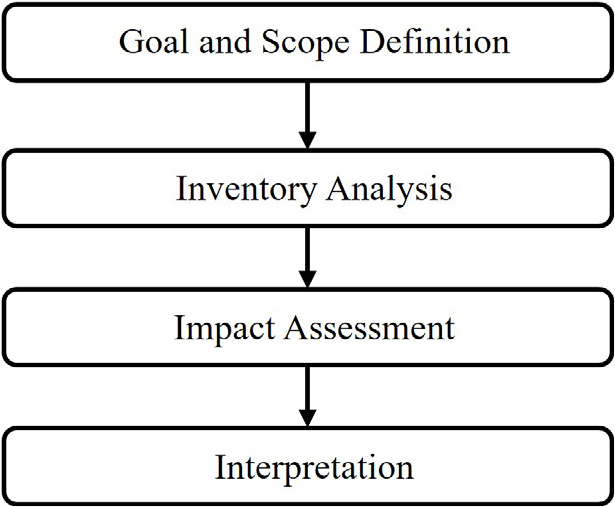
- As climate change intensifies, the frequency of natural disasters is increasing and greenhouse-gas (GHG) emissions from the industrial sector are becoming a critical concern. In response, many countries have declared a 2050 Net-Zero target based on IPCC reports and are strengthening carbon-reduction strategies in the infrastructure sector. In Korea, institutional foundations for GHG mitigation have also been established through the enactment of the Framework Act on Carbon Neutrality and Green Growth and its enforcement decree. Although emissions generated during tunnel construction are reported to have substantial environmental impacts, domestic studies have largely focused on a limited set of SOC facilities, and tunnel-specific literature remains scarce. Therefore, this study reviews domestic and international research trends related to tunnel construction emissions. Korea-specific emission factors applicable to this study were selected based on the 2024 National Greenhouse Gas Inventory Report and the 2024 Approved National GHG Emission Factors issued by the Ministry of Climate, Energy and Environment; where emission factors were not explicitly provided, they were estimated using the TOTAL Ver. 6.6.2 program developed by the Korea Environmental Industry & Technology Institute (KEITI). Using the derived emission factors, we adopted the framework and key assumptions of the CO2 emission calculation model proposed by prior international studies and developed a calculation model that quantifies CO2 emissions occurring during the construction phase of NATM tunnels, which directly drives GHG emissions, and CO2 emissions attributable to material use. Finally, the validity of the proposed equations was evaluated by comparing emission factors from prior studies with the Korea-specific emission factors derived in this study.
- COLLAPSE
기후변화로 인한 자연재해가 증가하고 산업부문 온실가스 배출 문제가 심화되면서, 각국은 IPCC 보고서 등을 바탕으로 2050 탄소중립(Net-Zero)을 선언하고 인프라 부문에서도 탄소 감축 전략을 강화하고 있다. 국내에서도 탄소중립기본법과 시행령을 제정하여, 온실가스 감축을 위한 다양한 정책 수단과 제도적 기반을 적극적으로 마련하고 있다. 터널 시공 중 발생하는 온실가스는 건설 산업 환경에 상당한 영향을 미친다고 보고되었으나 국내에서는 일부 SOC 시설을 대상으로 한 연구만 수행되었을 뿐 터널과 관련된 연구는 아직 미진한 실정이다. 이에 본 연구에서는 터널과 관련된 국내외 연구동향을 검토하였고, 2024 국가 온실가스 인벤토리 보고서와 기후에너지환경부의 2024 승인 국가 온실가스 배출 계수 문헌을 통해 국내 적용 가능한 국가 고유 배출계수를 선정하였으며, 정확히 명시되지 않은 배출계수의 경우 한국환경산업기술원에서 제공하는 TOTAL Ver. 6.6.2 프로그램을 활용하여 산정하였다. 산정된 배출계수를 활용하고, 기존 해외 논문에서 제시된 CO2배출량 계산 모델과 내용을 준용하여 온실가스 배출에 직접적인 영향을 미치는 NATM 터널의 시공 단계에서 발생되는 CO2배출량과 자재 사용으로 인해 발생되는 CO2배출량 계산 모델을 제시하였다. 또한 실증 검증이 완료된 기존 연구의 배출계수와 본 논문에서 제시한 국가 고유 배출계수를 비교 분석하여 제시한 산정식의 타당성을 검증하였다.
-
Proposal of a CO2 emission estimation equations based on the derivation of appropriate domestic emission factors and their application: Focusing on NATM tunnel LCA (A1-A5)
Journal Informaiton
 Journal of Korean Tunnelling and Underground Space Association
Journal of Korean Tunnelling and Underground Space Association
Journal Informaiton
Journal Informaiton - close
 Journal of Korean Tunnelling and Underground Space Association
Journal of Korean Tunnelling and Underground Space Association











